Table of Links
C. Comparison with Related Works
II. Background
C. Assumptions and Approximations
IV. Results
V. Discussion, Acknowledgments, and References
A. Algorithm
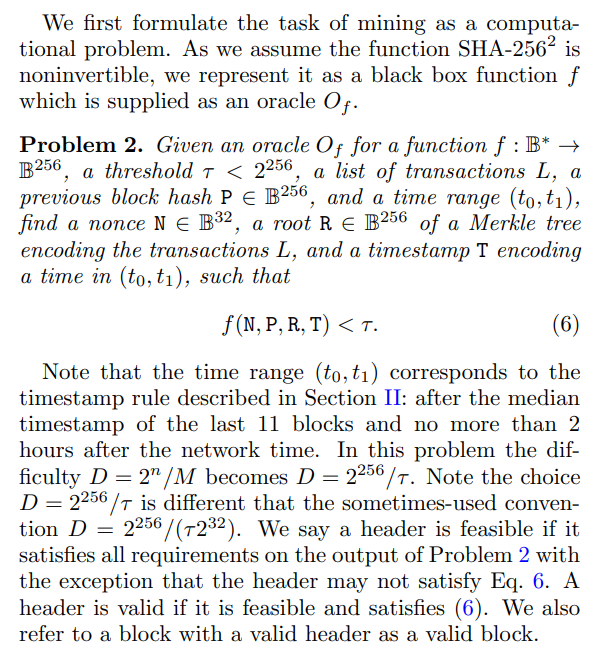
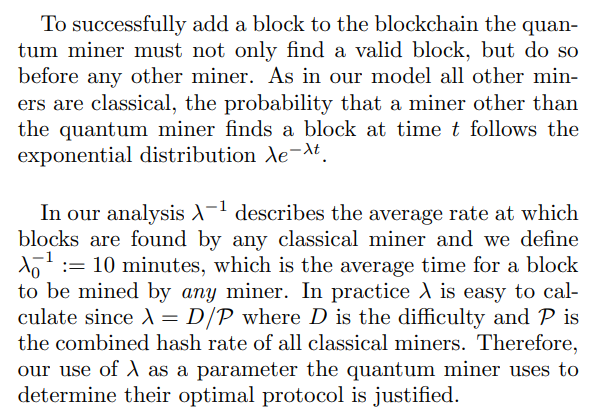
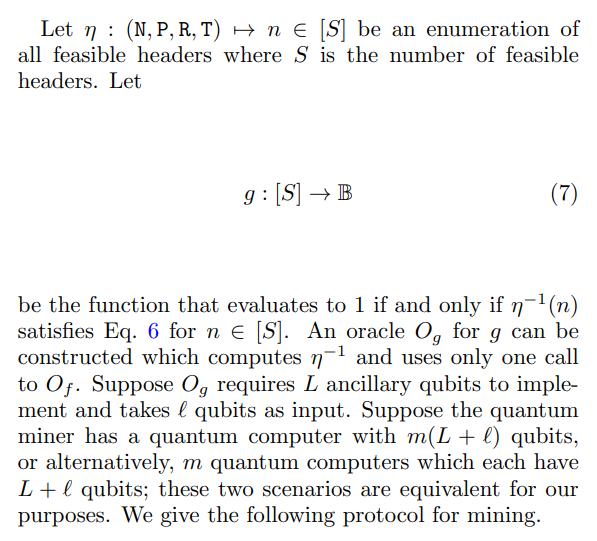


This algorithm contains two procedures, one for aggressive mining (agg = 1), and the other for peaceful mining (agg = 0). We consider both as peaceful mining is easier to analyze, and describes mining accurately in many scenarios, such as if the time to perform a measurement prohibits the quantum miner from effective aggressive mining. For both cases, we aim to determine the probability that the above procedure results in the quantum miner finding a marked header and that the resultant block gets accepted by the blockchain. We refer to this probability as the probability of success.
Authors:
(1) Robert R. Nerem, Institute for Quantum Science and Technology, University of Calgary, Alberta T2N 1N4, Canada ([email protected]);
(2) Daya R. Gaur, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Lethbridge, Alberta T1K 3M4, Canada.
This paper is

